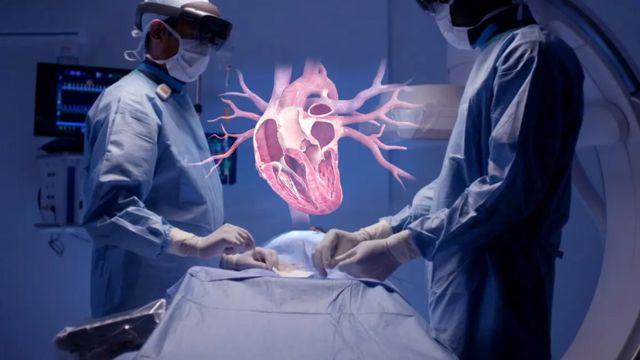
Medical practitioners in the always changing field of clinical engineering are depending more and more on technology to raise the efficiency and efficacy of their work. Among the most fascinating developments in this field is augmented reality (AR). Overlaying digital data onto the real environment, AR technology has great potential to transform the approach clinical engineers and medical professionals take to training, diagnostics, and maintenance.
Clinical engineering combines more sophisticated technologies, so engineers and healthcare professionals must adjust and learn how to run and fix innovative medical equipment. Although successful, conventional training approaches can fail to replicate real-world events in a regulated, risk-free setting. Here AR comes in handy, providing a highly engaging and immersive approach to learn, troubleshoot, and enhance clinical engineering techniques.
What is Augmented Reality?
In augmented reality (AR), digital elements—such visuals, music, and other sensory inputs—are combined into a live, real-world environment. AR improves the real world with further information that can be interacted with in real time, unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which generates a totally synthetic environment. AR is being used in healthcare to help with diagnosis, enhance training, and even aid clinical engineers through the difficult chore of medical device repairs.
You may like this: The Importance of User Training for Medical Supplies: Avoiding Common Mistakes
The Role of AR in Clinical Engineering Training
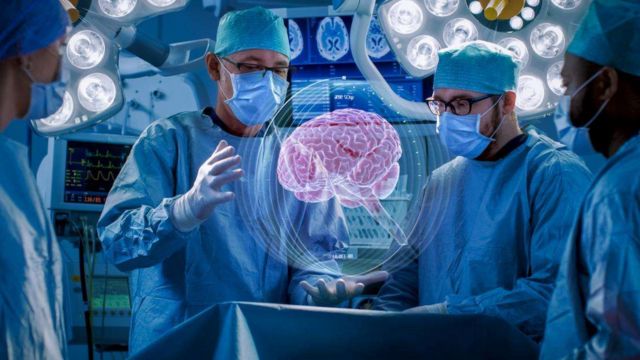
From the installation and calibration of medical equipment to guarantees of the safety and performance of devices used in hospitals and clinics, clinical engineering covers a broad spectrum of tasks. Clinical engineers must receive extensive training as the intricacy of medical equipment and their vital nature define their operation. AR is altering training methods as follows:
- Simulating Real-World Scenarios:
AR allows clinical engineers to experience real-world problems and scenarios without the risks associated with training on live equipment. For instance, engineers can use AR to simulate the malfunction of medical devices, learning how to troubleshoot and resolve issues without the fear of causing any real harm. This hands-on experience can significantly speed up the learning process and help engineers gain valuable practical knowledge. - Interactive Training Modules:
Traditional training often involves reading manuals or watching videos, but AR offers a more immersive experience. Clinical engineers can wear AR glasses or use tablets and smartphones to view interactive training modules that overlay helpful instructions, visual cues, and step-by-step guides directly onto the equipment they are working on. This allows engineers to see exactly what needs to be done, step by step, without needing to refer to external resources. - Remote Assistance and Collaboration:
AR can connect clinical engineers with experienced professionals through remote assistance features. If an engineer encounters a particularly tricky issue, they can use AR to share a live video feed of the device they are working on. Experienced engineers can then provide guidance or troubleshooting advice in real-time, even from across the world. This remote collaboration ensures that engineers have access to expert advice at all times, enhancing the speed and accuracy of their work.
Benefits of AR in Clinical Engineering
- Enhanced Learning:
AR creates an engaging learning environment where clinical engineers can interact with digital overlays to enhance their understanding of complex medical devices and systems. This visual and tactile learning approach improves retention and comprehension, making it easier for engineers to grasp difficult concepts. - Improved Accuracy and Efficiency:
By providing clinical engineers with on-demand guidance, AR can reduce errors in equipment repairs and maintenance. For example, when repairing a medical device, AR can highlight specific components that need attention, offer troubleshooting suggestions, and ensure that engineers follow the correct procedures. This reduces the likelihood of mistakes and increases the overall efficiency of clinical engineering operations. - Cost-Effective Training:
Traditional training often involves expensive simulators, travel expenses, or using real medical equipment for practice. AR can reduce these costs by providing a virtual training environment that replicates real-world conditions. This makes it easier for healthcare organizations to train large teams of clinical engineers without the financial burden of traditional training methods.
The Future of AR in Clinical Engineering
As AR technology continues to advance, its applications in clinical engineering will only become more widespread. Future trends include:
- AI-Enhanced AR Systems:
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) with AR could further enhance the training experience. AI could analyze an engineer’s actions in real-time, offering personalized feedback or adapting training scenarios based on their skill level. This intelligent guidance will ensure that engineers receive the most relevant training for their needs. - Real-Time Diagnostics and Repair:
AR could also be used for real-time diagnostics of medical equipment. By pairing AR with machine learning and IoT (Internet of Things) sensors, engineers could receive instant feedback on a device’s performance. If a malfunction occurs, AR could highlight the problem areas on a digital overlay and provide step-by-step instructions on how to fix the issue, enhancing diagnostic speed and accuracy. - Global Training Platforms:
As more healthcare institutions adopt AR technology, we could see the development of global training platforms where clinical engineers from around the world can collaborate, learn, and share knowledge. This global network will ensure that engineers have access to the latest insights, trends, and best practices in the field of clinical engineering.
You may like this: How Clinical Engineers Handle the Integration of New Technologies with Legacy Medical Equipment
Conclusion
Including augmented reality into clinical engineering education marks a radical change in how clinical engineers and healthcare professionals will be taught going forward. AR promises to improve accuracy, save costs, and hasten the learning process by means of its capacity to offer hands-on, immersive experiences in a controlled setting. Future even more creative uses that will simplify processes and enhance patient care are expected as the technology develops. Augmented reality is driving the technological revolution that clinical engineering is about to start.
At JandJ Supplies, we are dedicated to keep you updated on the most recent developments in clinical engineering & medical supplies. Maintaining your staff always on top of technology requires constant updating with the newest industry trends, training tools, and insights. Subscribe right now to our newsletter for consistent updates, professional advice, and more!