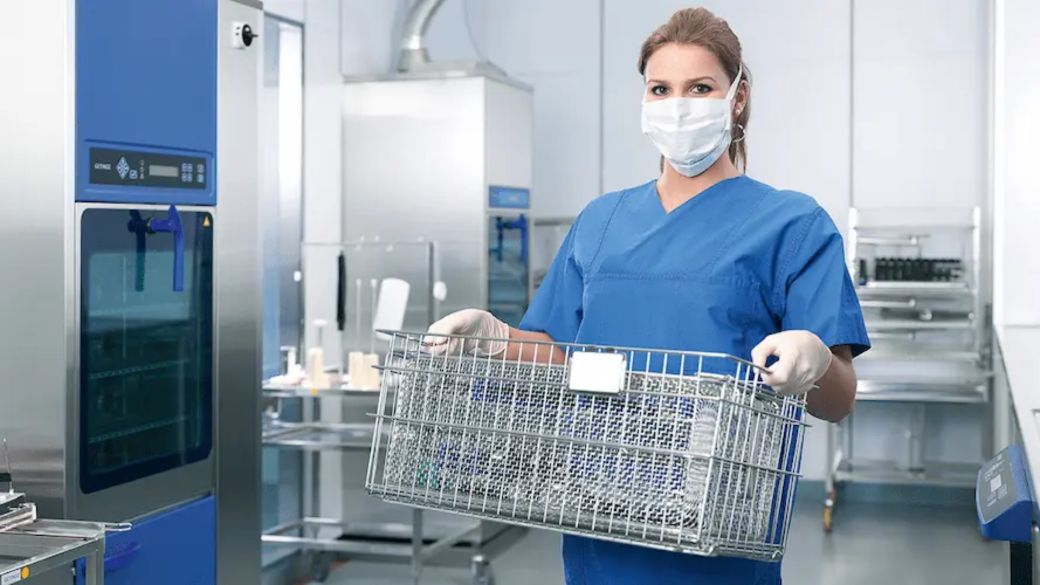
Ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical supplies is of great relevance in the medical domain. Sterilization is absolutely important if we are to keep the best standards in healthcare. From medical tools, equipment, and supplies, sterilisation is the process of totally eradicating all microbiological life—including bacteria, viruses, fungus, and spores. Medical supplies used in hospitals, clinics, and healthcare environments must be free from germs that can possibly cause diseases. Let us explore the significance of sterilisation in medical supplies and the reasons behind its indispensible presence in contemporary healthcare methods.
1. Preventing Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAIs)
The fact that sterilisation helps to prevent healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) explains one of the main reasons it is so crucial. The Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) define HAIs as infections individuals pick up while under treatment for another illness. With medical equipment as the main source of transmission, these illnesses account for a major global morbidity and death load. Medical supplies including surgical tools, catheters, or any reusable equipment that are improperly sterilised could introduce dangerous bacteria, viruses, or fungus into a patient’s body and cause an illness. For example, inadequate sterilising of surgical tools can cause surgical site infections, often severe and capable of delaying recovery or causing further difficulties.
By guaranteeing that microorganisms do not compromise the tools used in operations, tests, and patient care, sterilisation helps to lower the risk of HAIs and thereby increase patient safety.
2. Ensuring Patient Safety
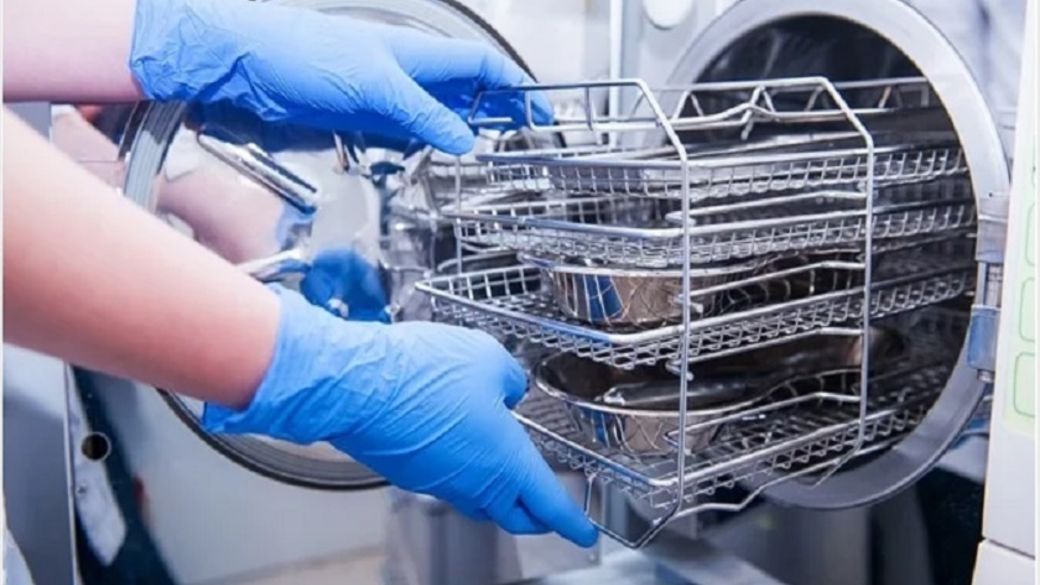

In healthcare, patient safety takes front stage. Maintaining free from hazardous bacteria medical supplies used on patients—especially those used in invasive operations—is directly dependent on sterilisation. Scalpels, forceps, and needle holders are among surgical tools that directly touch interior tissues therefore any contamination could have disastrous effects. If improperly sterilised, even little, non-invasive tools like thermometers, blood pressure cuffs, and stethoscopes can harbour bacteria.
Making ensuring these tools do not spread diseases depends on a strong sterilising mechanism. One should underline that sterilisation is not the same as disinfection and cleaning. Only sterilisation ensures the whole eradication of infections, while cleaning removes dirt and obvious pollutants and disinfection lowers the number of germs. For medical supplies used routinely or in vital operations, where patient safety directly influences, this is especially crucial.
3. Types of Sterilization Methods
The type of medicinal supply and the material it is derived from determine the sterilising technique applied. Knowing these strategies helps one to guarantee the correct approach for every object:
-
Autoclaving (Steam Sterilization):
This is the most common method of sterilization used in healthcare settings. Autoclaving uses high-pressure steam at temperatures typically around 121-134°C. This method is effective for sterilizing surgical instruments, gowns, and other heat-resistant medical supplies. Autoclaving is quick, efficient, and can handle large volumes of instruments. -
Ethylene Oxide (EO) Sterilization:
For heat-sensitive materials, such as plastic medical devices or electronic components, ethylene oxide gas is used. EO sterilization occurs at lower temperatures, making it ideal for equipment that cannot withstand the heat from autoclaving. However, EO sterilization requires a longer exposure time and careful handling due to the toxicity of the gas. -
Dry Heat Sterilization:
This method involves sterilizing medical supplies by exposing them to hot air in a dry heat oven. It is typically used for sterilizing glassware or materials that may be damaged by steam. The high temperature (usually between 160°C to 180°C) ensures the destruction of microorganisms. -
Radiation Sterilization (Gamma or E-Beam):
For single-use disposable items, gamma radiation or electron beam radiation is used to sterilize the products. This method is non-thermal and ideal for materials sensitive to heat or moisture. Radiation sterilization is widely used for sterilizing items like surgical gloves, syringes, and wound dressings. -
Hydrogen Peroxide Plasma Sterilization:
This method is used for sensitive instruments, including endoscopes and surgical tools. Hydrogen peroxide plasma sterilization involves converting hydrogen peroxide into a plasma state, which eliminates microorganisms without the use of high temperatures or harmful chemicals.
4. Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Not only does sterilisation provide patient safety, but it is also a controlled activity used in hospitals. Many companies, including the FDA (Food and Drug Administration), CDC, and the World Health Organization (WHO), offer rigorous standards for sterilising techniques and certification of sterilisation operations. Medical facilities have to follow these guidelines in order to guarantee they are delivering competent and safe treatment.
ISO 13485 is also an international standard defining specifications for medical device design, manufacture, and sterilisation. Medical supply manufacturers have to satisfy these strict criteria, which include comprehensive guidelines for sterilising techniques, therefore guaranteeing that the goods are safe for clinical usage.
5. Sterilization and Infection Control Protocols
Infection control strategies in hospitals, offices, and other healthcare environments depend critically on sterilisation. Working collaboratively with healthcare providers, infection control teams create and maintain sterilisation procedures to guarantee that every piece of medical equipment is sterilised using the proper technique and that every staff member follows safety policies. Effective sterilising techniques help to stop hospital-acquired illnesses from spreading, therefore sparing susceptible people from terrible effects.
Moreover, monitoring sterilisation cycles and making sure that all equipment is correctly sterilised between usage helps establish a culture of responsibility and safety in medical surroundings.
6. Conclusion
In essence, sterilisation in medical supplies is a necessary habit in contemporary healthcare that guarantees patient safety, avoids infections, and conforms with legal criteria. Effective sterilising techniques for various medical supplies help healthcare professionals greatly lower the risk of healthcare-associated infections, therefore protecting patients and employees. Maintaining strong standards of patient care and safety depends on keeping strict sterilisation procedures as medical technology develops.
Stay informed and up-to-date with expert insights on medical supplies, clinical engineering, and manufacturing. At JandJSupplies, we provide comprehensive educational resources to help you understand critical healthcare and industrial topics. Explore our articles, guides, and tips to enhance your knowledge today!